This Tutorial explains how to configure a RevPi base module as a Modbus RTU Slave using a USB-RS485 Converter. It includes detailed steps to set up the connection and query data from the RevPi using a Modbus RTU Master.This Tutorial is for industrial automation professionals, IoT developers, and others needing to integrate RevPi as a Modbus RTU Slave in their systems.
Prerequisites #
Hardware #
-
RevPi base module (eg.RevPi Connect 4)
-
Master device or software: For example, “qModMaster” on a Windows PC.
-
USB-RS485 Converter
-
Cables and connectors for RS485 communication
Software #
-
A modern web browser (e.g., Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox).
-
qModMaster: Downloadable from SourceForge.
RS485 Signal Connections #
| Signal | Pin |
|--------|------|
| RS485- | D+ |
| RS485+ | D- |
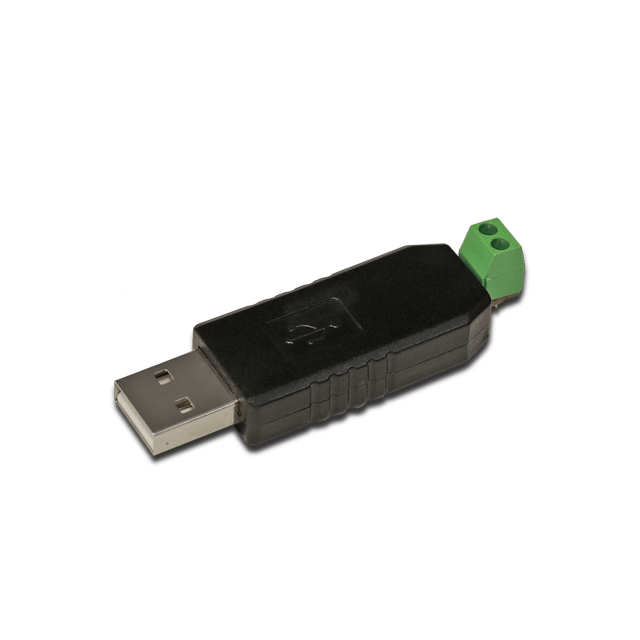

Step 1: Hardware Setup #
-
Connect the USB-RS485 Converter to the RevPi Connect.
-
Wire the RS485+ and RS485- signals appropriately to your devices.
-
Ensure power is supplied to the RevPi Connect.
Step 2: Configure Modbus RTU Slave in PiCtory #
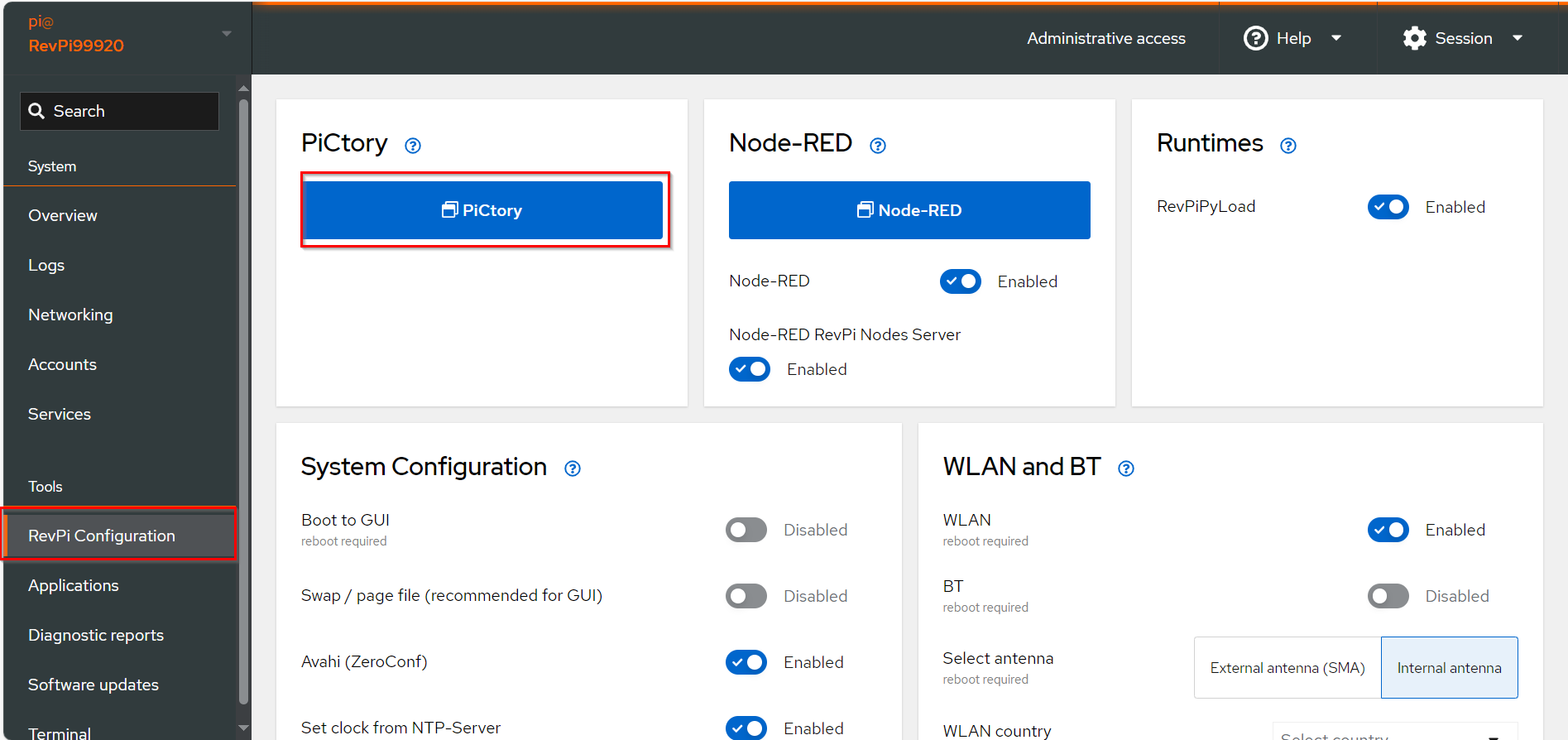
▷ Drag the base module from the Device Catalog onto the virtual DIN rail.
▷ Open the folder Virtual Devices in the Device Catalog.
-
Drag Modbus RTU Slave to the base module on the virtual DIN rail.
❯ The Modbus RTU Slave will now appear in the configuration
-
Select the Modbus RTU Slave in the configuration.
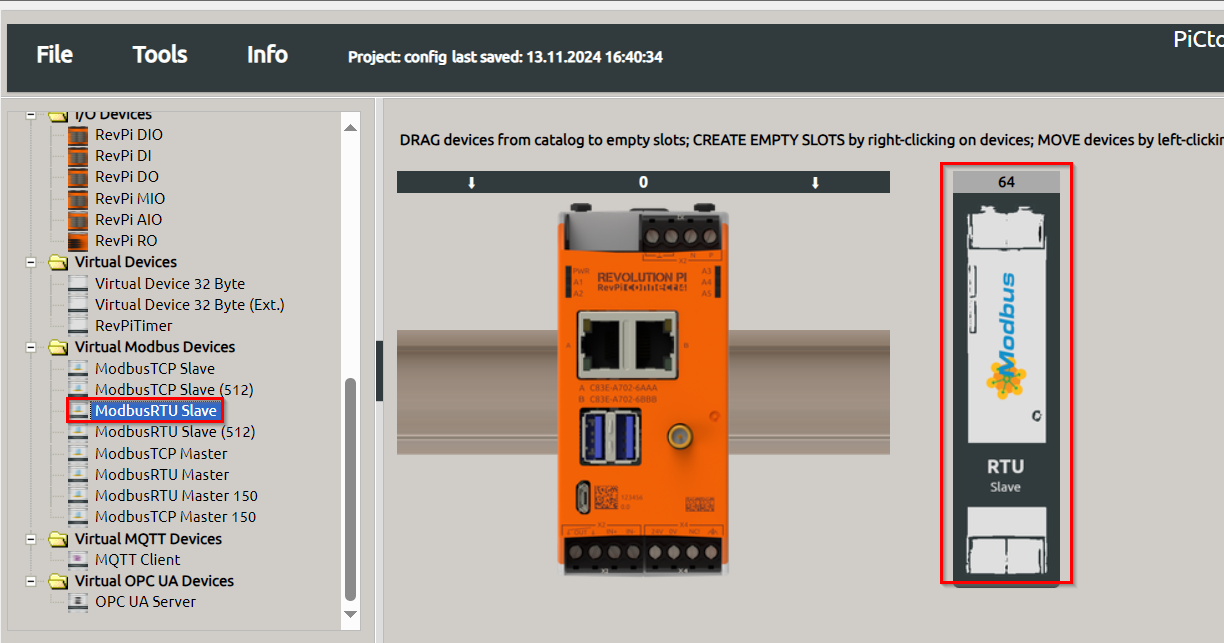
-
Set the following parameters in the Value Editor:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Input |
Configure up to 32 input values, each 16 bits wide. |
Output |
Configure up to 32 output values, each 16 bits wide. |
device_path |
Path to the Linux device file, default: |
baud_rate |
Speed of the serial connection, default: |
parity |
Configure parity bit: None, Even (default), or Odd. |
data_bits |
Number of data bits, default: |
stop_bits |
Number of stop bits, default: |
|
Note
|
If using multiple devices of the same type, configure unique udev rules to prevent device path conflicts after reboot. |
Step 3: Querying Data Using qModMaster #
-
Start qModMaster on the Windows PC.
-
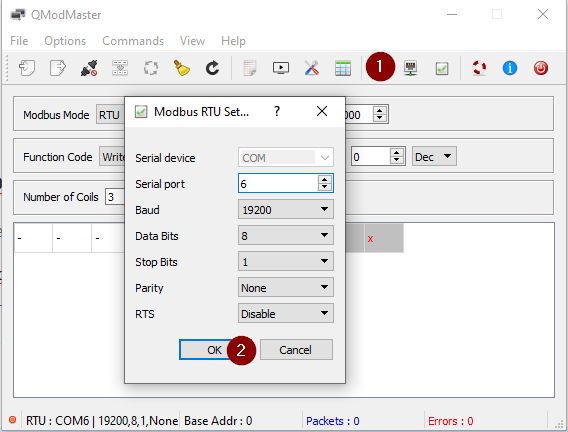
Configure Serial Interface Parameters
Set the parameters for communication to match the Modbus RTU Slave configuration:-
Baud rate, parity, stop bits, and data bits.
-
-
Transfer Data to Modbus Registers
Use qModMaster to write values (e.g., 1, 2, 3) into the Modbus registers.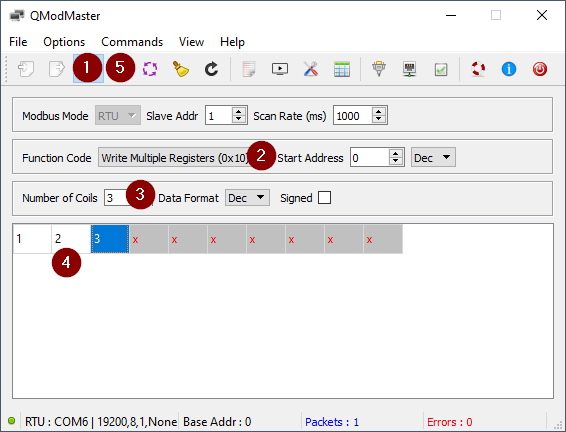
-
Query Data from RevPi Shell
Use thepiTestcommand to query data from the Modbus RTU Slave:piTest -1 -r Input_1Example Output:
2 Byte-Value of Input_1: 1 dez (=0001 hex) piTest -1 -r Input_2 2 Byte-Value of Input_2: 2 dez (=0002 hex) piTest -1 -r Input_3 2 Byte-Value of Input_3: 3 dez (=0003 hex)
Notes and Best Practices #
-
Device Path Conflicts: To avoid issues when rebooting, configure udev rules to assign consistent paths to the device files.
-
Baud Rate: Ensure the master and slave devices are configured with matching baud rates for proper communication.